Zultys - Network / IT Requirements (On-Premise)
A premise phone system, also known as an on-premises phone system or Private Branch Exchange (PBX), is a telecommunications solution where all the hardware and infrastructure are located within a business's physical location or premises. Unlike hosted phone systems that rely on remote servers, a premise system operates independently within the organization's own network. It offers greater control and security over the telecommunication infrastructure but typically requires a significant upfront investment in hardware and maintenance. Users connect to the premise system through physical desk phones or software clients. While premise systems provide a high level of customization and reliability, they may lack the scalability and remote work capabilities of cloud-based alternatives.
Overview
Requirements
- All Required Ports Forwarded or Placed in a DMZ: To ensure seamless communication with the hosted phone system, it's crucial to forward the necessary ports or place the system in a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone). This step allows external access while maintaining security.
- Stable Internet Connection: A reliable and stable internet connection is fundamental, especially when accessing the system remotely or via mobile applications. Consistent internet connectivity is essential for dependable communication.
- Ability to Install Required Software: Users must have the ability to install the required software on their computers. This may require domain login with Administrator access, IT assistance, or access by a local administrator to ensure proper software installation and configuration.
- SIP ALG Disabled: To prevent potential interference with VoIP traffic, SIP Application Layer Gateway (ALG) should be disabled on your network devices.
- Avoid CG-NAT or Double NAT (Only if Accessing Remotely/Using Mobile Applications): When accessing the system remotely or via mobile apps, it's advisable to avoid Carrier-Grade Network Address Translation (CG-NAT) or double NAT setups (multiple routers in series), as these can complicate VoIP traffic routing.
Recommendations
- Managed Network Equipment: Consider using managed network equipment from reputable brands like Cisco, Ubiquity, or Juniper. This provides greater control over your network, including Quality of Service (QoS) settings, ensuring that VoIP traffic receives priority for optimal call quality.
- Static WAN IP Address (Dynamic DNS): While a static WAN IP address is preferred, dynamic DNS (DDNS) can be used as an alternative. DDNS allows for consistent remote access even if your IP address changes, enhancing accessibility.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) Network Switches: If applicable to your setup, PoE switches simplify power management, especially when dealing with VoIP phones or other powered devices in remote locations.
- Voice VLAN for Traffic Segmentation: Implementing a dedicated Voice VLAN for traffic segmentation helps separate voice traffic from data traffic, ensuring a dedicated path for voice packets and maintaining call quality, whether in the office or remote locations.
- QoS Configuration: If you have managed network equipment, configure Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your firewall and switches. This prioritizes VoIP traffic, guaranteeing a smooth and uninterrupted calling experience for remote and mobile users.
- Company SMTP Server/Relay: While not specific to remote access, having your own SMTP server or relay, which you provide by default, enhances email communication within the phone system, including notifications and voicemail delivery.
By adhering to these network requirements and recommendations, your hosted phone system will not only function efficiently but also ensure a seamless experience for remote users and those using mobile applications, maintaining high-quality voice communication.
Networking Information
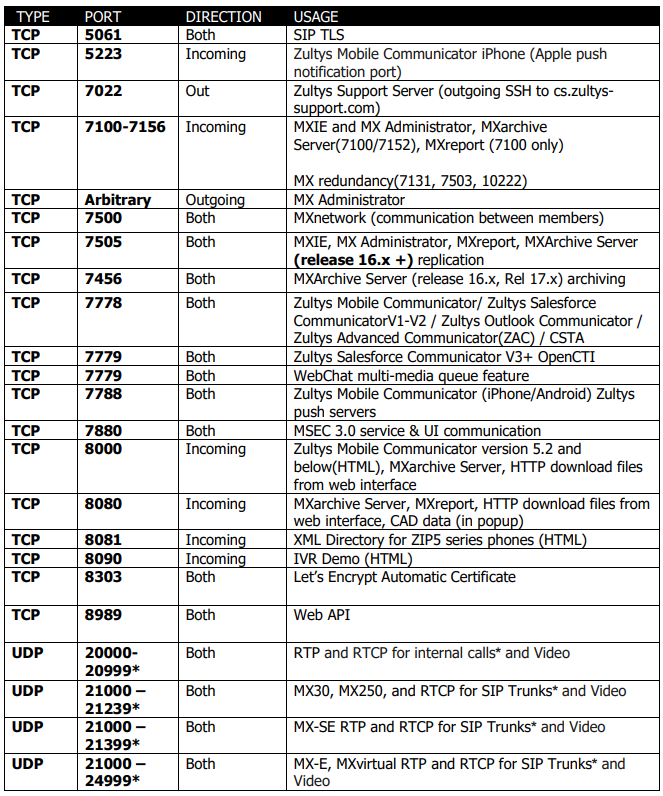
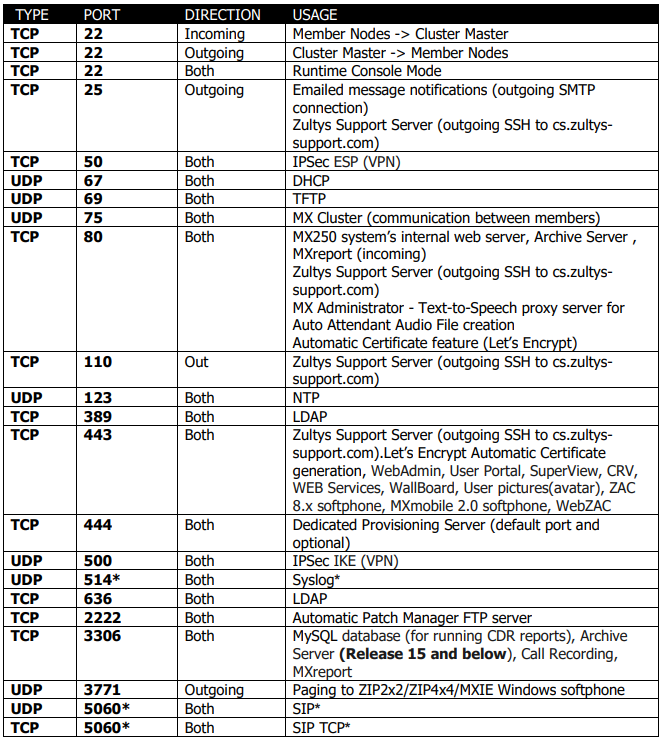
Ports / Firewall Rules
Phone System
Incoming = Incoming on the Phone System
Outgoing = Outgoing from Phone System
MXIE Client
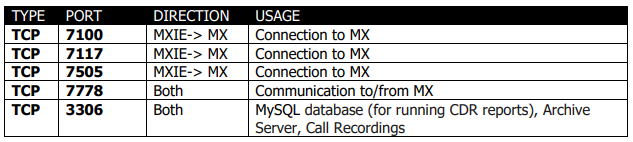


*Indicates that the port can be changed.
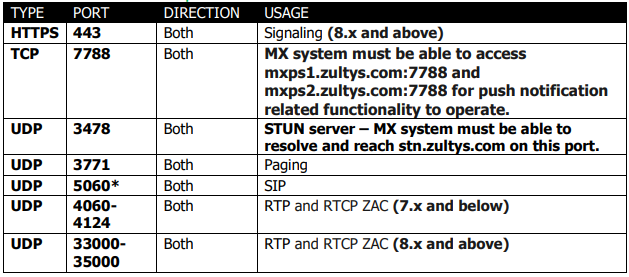
ZAC Client

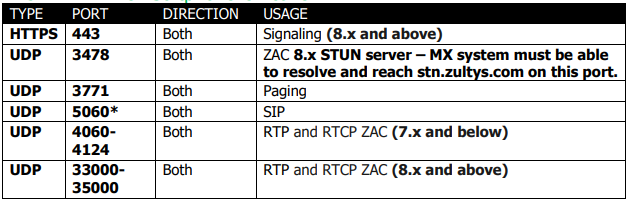
*Indicates that the port can be changed on ZAC versions 7.x and below. On ZAC versions 8+ this port CANNOT be changed.
WebZAC
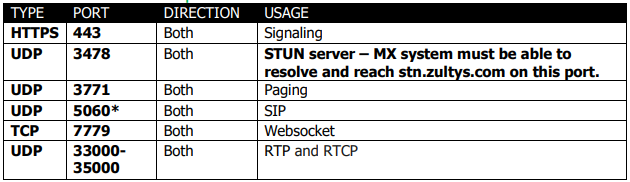
MXmobile 2.0 iPhone
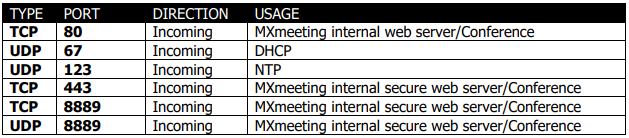
MXmeeting
MG Gateway
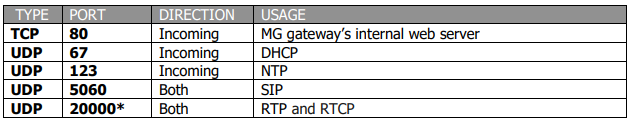
*Indicates that the port can be changed.
Phones
ZIP 5 SIP Phones
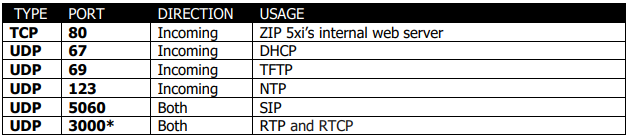
*Indicates that the port can be changed.
ZIP 3x SIP Phones
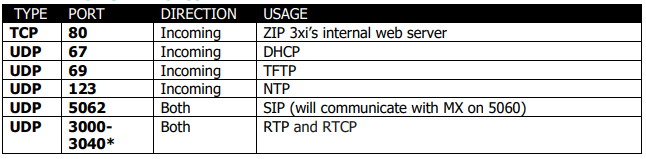
*Indicates that the port can be changed.
ZIP 4x SIP Phones
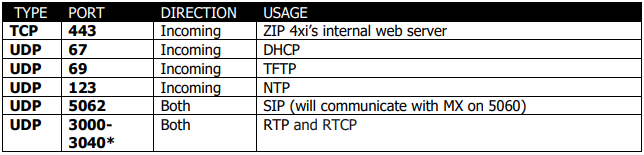
*Indicates that the port can be changed.
Z 2x SIP Phones
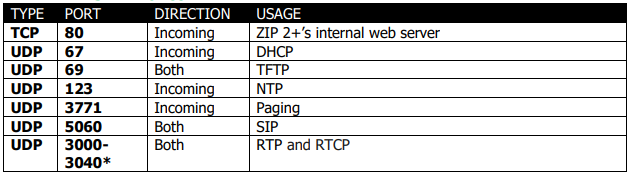
*Indicates that the port can be changed.
